Lipoma Treatment: When Surgery is Necessary
Lipoma treatments in Dubai are benign tumors made up of fatty tissue that develop just under the skin. They are usually soft, movable, and painless, and often go unnoticed unless they become large or are in a prominent location. While lipomas are generally harmless and don’t pose a serious health risk, certain circumstances may warrant surgical intervention. This article explores the situations when surgery becomes a necessary option for treating lipomas and what patients need to know about the procedure.
Indications for Lipoma Surgery
Surgical removal of a lipoma may be considered for several reasons, including:
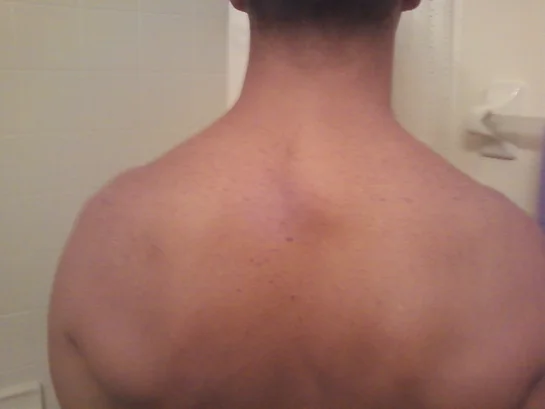
- Size and Growth: When a lipoma grows significantly large, it may become more noticeable and potentially uncomfortable. Large lipomas, particularly those that exceed a few centimeters in diameter, are often removed to alleviate discomfort and prevent further growth. Even if the lipoma is not causing pain, its size may prompt patients to seek surgery for cosmetic reasons.
- Location: Lipomas located in areas where they interfere with movement or cause functional issues may require surgical removal. For example, a lipoma on the back, shoulder, or arm could hinder normal movement or cause friction with clothing, leading to discomfort or irritation.
- Pain and Discomfort: Although lipomas are typically painless, some may cause discomfort if they press against nerves or other tissues. In such cases, surgical removal can provide relief from pain and improve quality of life.
- Cosmetic Concerns: Lipomas that are visible and affect a person's appearance can lead to self-consciousness and emotional distress. For cosmetic reasons, patients may choose to undergo surgery to improve their appearance and restore self-confidence.
- Diagnostic Uncertainty: Occasionally, a lipoma may be examined to ensure it is indeed benign and not indicative of a more serious condition. Surgery may be recommended if there is any uncertainty about the diagnosis or if there are changes in the lipoma that warrant further investigation.
- Recurrence: If a lipoma recurs after a previous attempt at non-surgical treatment or if it does not respond to other interventions, surgical removal might be necessary to address the issue effectively.
Types of Surgical Procedures for Lipomas
Several surgical techniques can be used to remove a lipoma, depending on its size, location, and the patient’s overall health.
1. Excision
Excision is the most common surgical method for removing lipomas. The procedure involves making an incision over the lipoma, carefully removing it along with its capsule, and then closing the incision with sutures. Excision ensures that the entire lipoma is removed, minimizing the risk of recurrence.
Procedure Details:
- Anesthesia: The procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia, which numbs the area around the lipoma.
- Recovery: Recovery time is typically short, with most patients resuming normal activities within a few days. The incision site may be tender and swollen initially, but these symptoms usually subside within a few weeks.
2. Liposuction
Liposuction can be used as an alternative to traditional excision, especially for larger lipomas or those located in challenging areas. This technique involves inserting a thin tube (cannula) into the lipoma and using suction to remove the fatty tissue.
Procedure Details:
- Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is used to numb the area where the liposuction will be performed.
- Recovery: Liposuction generally has a shorter recovery time compared to excision, but there may be a risk of incomplete removal or recurrence. Follow-up may be needed to ensure that the lipoma has been adequately addressed.
3. Laser Surgery
Laser surgery is a less common but effective method for treating lipomas. It involves using focused laser light to break down the fatty tissue. This technique is usually reserved for specific cases and may offer benefits such as reduced bleeding and shorter recovery time.
Procedure Details:
- Anesthesia: The procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia.
- Recovery: Laser surgery may result in less postoperative discomfort and scarring compared to traditional excision.
Post-Surgery Care
After surgery, proper care is crucial to ensure optimal healing and prevent complications. Patients should follow these guidelines:
- Wound Care: Keep the surgical site clean and dry. Follow any instructions provided by the healthcare provider regarding wound care, including changing dressings and monitoring for signs of infection.
- Pain Management: Mild pain or discomfort is normal after surgery. Over-the-counter pain relievers or medications prescribed by the healthcare provider can help manage these symptoms.
- Activity Restrictions: Patients may need to avoid strenuous activities and heavy lifting for a period after surgery to prevent complications and promote healing.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Attend all scheduled follow-up appointments to monitor the healing process and ensure that the lipoma has been completely removed. The healthcare provider will assess the surgical site and address any concerns.
- Monitor for Complications: Watch for any signs of complications, such as increased redness, swelling, or discharge from the wound. Contact the healthcare provider if any unusual symptoms arise.
Potential Risks and Complications
As with any surgical procedure, there are risks associated with lipoma removal. These may include:
- Infection: Though rare, infections can occur at the site of surgery. Proper wound care and following medical advice can help minimize this risk.
- Recurrence: There is a possibility that the lipoma may recur, especially if it was not completely removed. Follow-up care is essential to address any recurrence promptly.
- Scarring: Surgical removal may result in scarring. The extent of scarring depends on the size and location of the lipoma and the technique used. The healthcare provider can offer guidance on minimizing scarring.
- Nerve Damage: Although uncommon, there is a slight risk of nerve damage during surgery, which can lead to numbness or tingling in the surrounding area.
Conclusion
Surgery for lipoma removal is often necessary when the lipoma causes discomfort, interferes with function, or affects appearance. Understanding when surgery is the appropriate option and the types of procedures available can help patients make informed decisions about their treatment. By following post-surgical care guidelines and addressing any concerns with a healthcare provider, patients can achieve successful outcomes and restore their quality of life.
4o mini